🔄 LEC-6: What Happens When You Turn On Your Computer?
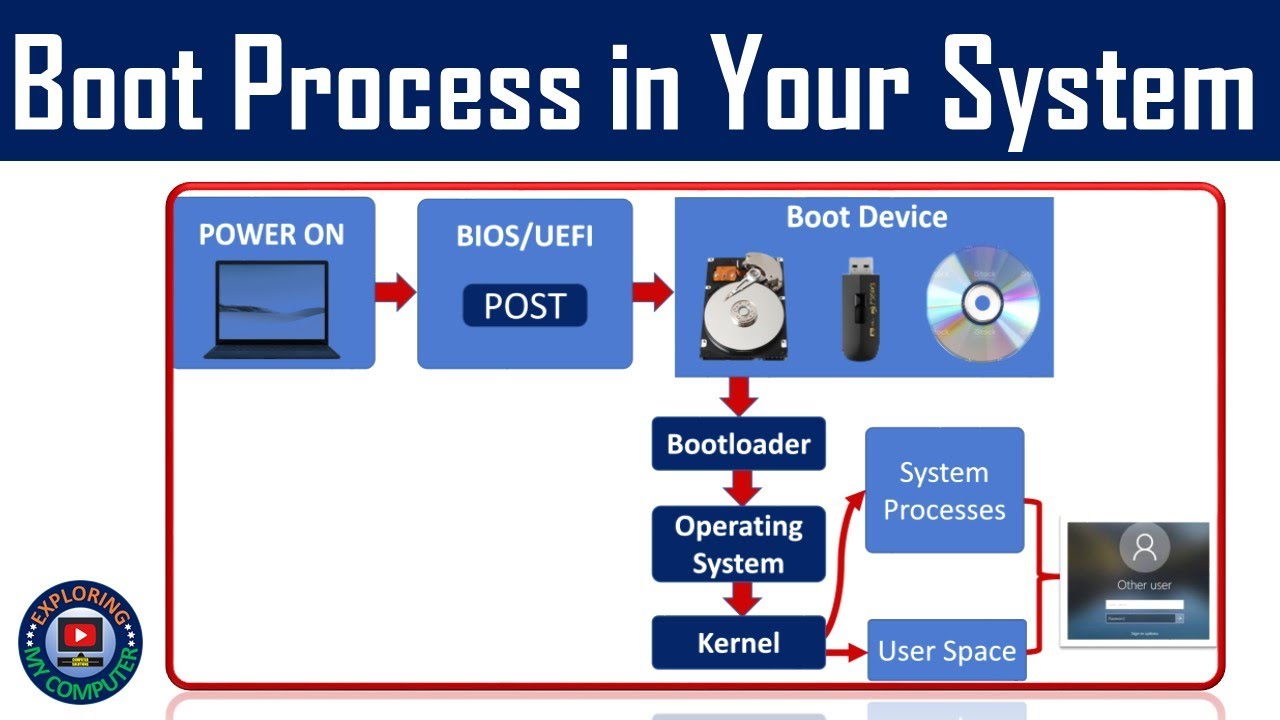
Step-by-Step Boot Process
| Step | Description | Example / Analogy |
|---|---|---|
| 1Power ON | You press the power button. Electricity flows to the motherboard. | Like switching on a car. |
| 2POST (Power-On Self-Test) | BIOS/UEFI checks hardware (keyboard, RAM, hard disk) for basic functionality. | Like a pilot checking engine, wings, etc. before flying. |
| 3BIOS/UEFI Loads | Basic firmware stored in ROM. Finds bootable devices (HDD, SSD, USB). | It's the "start-up brain" of the motherboard. |
| 4Bootloader Loads | BIOS finds and runs bootloader (like GRUB, Windows Boot Manager) from disk. | Bootloader is like a traffic cop directing where the OS is. |
| 5OS Loads into RAM | Bootloader loads OS kernel (Windows/Linux/macOS) into RAM. | Like reading instructions (OS) from a book (disk) into your brain (RAM). |
| 6System Starts | OS initializes services, drivers, login screen appears. | You're ready to work now! |
🧠 Interview Tip:
Q: What is the role of BIOS?
A: BIOS performs hardware checks and loads the bootloader which then loads the OS.
💻 LEC-7: 32-Bit vs 64-Bit OS
Key Differences
| Feature | 32-bit OS | 64-bit OS |
|---|---|---|
| Registers | 32-bit | 64-bit |
| Max RAM | ~4 GB | ~18 Quintillion GB (theoretical) |
| Speed | Processes 4 bytes/cycle | Processes 8 bytes/cycle |
| Compatibility | Runs only 32-bit apps & OS | Runs both 32-bit & 64-bit apps/OS |
| Performance | Slower for heavy apps | Better for gaming, video editing, etc. |
🔧 Real-World Example:
A PC with 8GB RAM and 64-bit processor:
- If you install a 32-bit OS, only 4GB RAM will be used.
- With 64-bit OS, full 8GB RAM is utilized.
🧠 Interview Tip:
Q: Why can't a 32-bit OS use more than 4GB RAM?
A: Because it can only generate 2³² (4,294,967,296) memory addresses = 4GB.
💾 LEC-8: Storage Devices & Memory Hierarchy
Memory Types (From Fastest to Slowest)
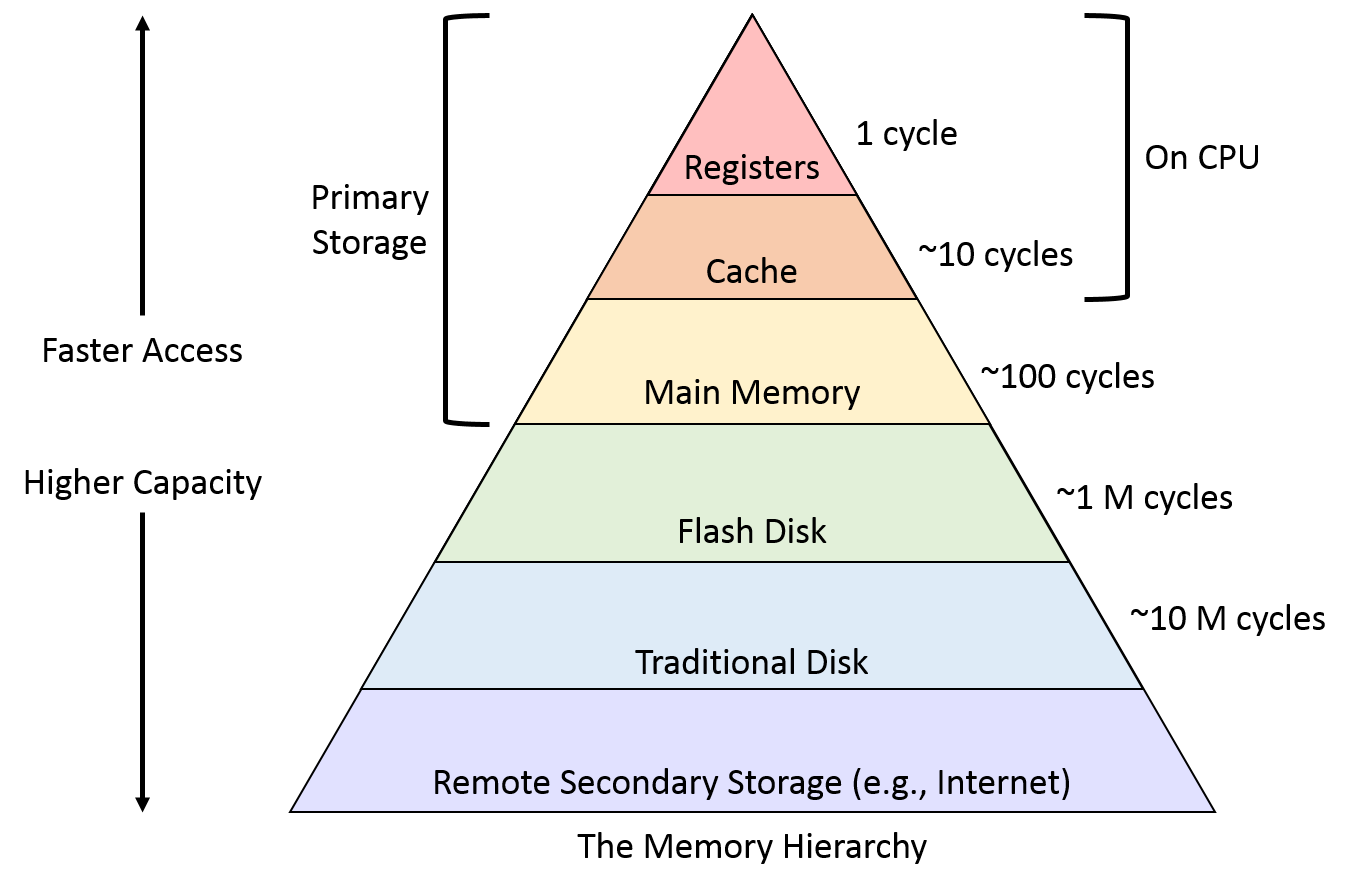
| Memory Type | Description | Speed | Size | Volatile? |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Register | Built into CPU. Holds small bits of data like instructions. | Fastest | Few Bytes | Yes |
| Cache | Fast memory near CPU. Stores frequently used data. | Very Fast | KB to MB | Yes |
| RAM (Main Memory) | Temporary workspace for CPU. Apps and OS load here. | Fast | GBs | Yes |
| Secondary Storage | Hard drives, SSDs. Permanent storage. | Slowest | TBs | No |
🧠 Interview Tip:
Q: Why is cache faster than RAM?
A: Cache is physically closer to the CPU and built with faster memory (SRAM vs DRAM in RAM).
✅ Quick Summary (Super Revision)
💡 What Happens When You Turn On Your Computer?
- Power → POST → BIOS → Bootloader → OS Loads → Ready to Use
💡 32-bit vs 64-bit
- 32-bit: Max 4GB RAM, slower
- 64-bit: Handles more RAM, faster, supports both 32 & 64-bit apps
💡 Memory Types
- Registers > Cache > RAM > Secondary Storage
- Faster = Smaller & Costlier
- Primary memory = Volatile
- Secondary memory = Non-volatile
🧪 Interview Quick Questions
1. What is the role of BIOS in booting?
2. Explain POST.
3. Difference between 32-bit and 64-bit OS.
4. Why 32-bit OS can't use more than 4GB RAM?
5. What are registers? Why are they fast?
6. What is the difference between Cache and RAM?
7. What is volatile and non-volatile memory?
8. Arrange these in order of speed: HDD, Register, RAM, Cache.
9. How does the CPU use cache memory?
10. Can you install 64-bit OS on 32-bit CPU?